ATT&CK for Enterprise – TA0008 Lateral movement
Lateral Movement, Tactic TA0008 – Enterprise | MITRE ATT&CK®
“Lateral Movement” in cybersecurity refers to the technique attackers use to navigate and control a network after gaining initial access, often through a low-privileged user account. This stage involves exploiting vulnerabilities (like PrintNightmare), using legitimate credentials (through methods like “pass the ticket” or “pass the hash”), or installing remote access tools to move stealthily towards valuable targets, such as sensitive data or high-privilege accounts. This blog will explore and categorize specific alerts from Lateral movement alerts documentation.
T1210 Exploitation of Remote Services
| External ID | Name | Sev. | Description |
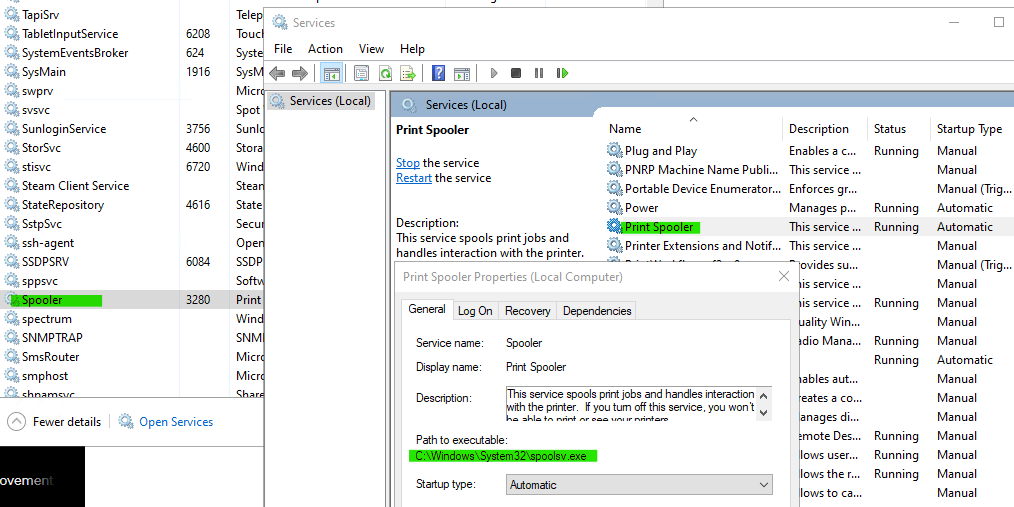
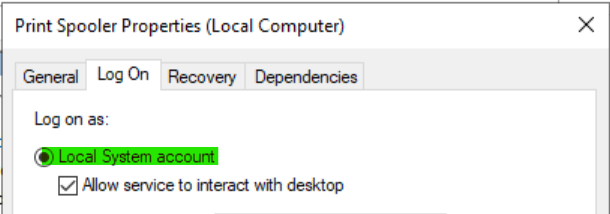
| 2415 | Suspected exploitation attempt on Windows Print Spooler service ① | High or Medium | Target: Windows Print Spooler service. Method of Attack: Adversaries exploit this service to carry out privileged file operations improperly. Requirements for the Attack: The attacker needs the ability to execute code on the target system. Successful exploitation of a vulnerability in the Print Spooler service. Impact of Successful Exploitation: The attacker can run arbitrary code with SYSTEM privileges on the target system. If the attack is against a domain controller, even a compromised non-administrator account can perform actions as SYSTEM. Consequences: This attack effectively allows any attacker who gains access to the network to quickly elevate their privileges to Domain Administrator. It enables the attacker to steal all domain credentials. The attacker can distribute further malware while operating with Domain Admin privileges. |
| 2036 | Remote code execution attempt over DNS | Medium | Vulnerability Identification: CVE-2018-8626, published by Microsoft on 12/11/2018. Affected Systems: Windows Domain Name System (DNS) servers. Nature of Vulnerability: Servers fail to properly handle requests, leading to a remote code execution vulnerability. Attack Mechanism: An attacker can exploit this vulnerability to run arbitrary code. The code runs in the context of the Local System Account, which has extensive privileges. Risk Scope: All Windows servers configured as DNS servers are vulnerable. Detection: Microsoft Defender for Identity security alert triggers when DNS queries suspected of exploiting CVE-2018-8626 are made against a domain controller in the network. |
| 2039 | Suspected NTLM authentication tampering | Medium | Vulnerability Reference: The attack is based on the security vulnerability CVE-2019-1040 discovered in June 2019 by Microsoft. Attack Type: It involves a “man-in-the-middle” technique that targets the NTLM (NT LAN Manager) authentication protocol used in Windows. Bypassing NTLM MIC Protection: Attackers exploit this vulnerability to bypass the NTLM Message Integrity Check (MIC) ② , a security feature designed to prevent tampering with authentication messages. (It’s a NTLM V2 feature) Downgrading NTLM Security: The attack allows malicious actors to downgrade certain NTLM security features. Unauthorized Authentication: Exploiting this vulnerability enables attackers to create authenticated sessions impersonating other user accounts. |
| 2037 | Suspected NTLM relay attack (Exchange account) | Medium or Low if observed using signed NTLM v2 protocol ③ | Exploitation of Exchange Server: The attack involves configuring an Exchange Server computer account to initiate NTLM authentication with a remote HTTP server controlled by the attacker. Relaying Authentication Requests: The attacker’s server waits for communication from the Exchange Server, with the intent to relay the Exchange Server’s sensitive authentication information to another server, or more critically, to Active Directory over LDAP. Capturing Authentication Details: Once the relay server receives the NTLM authentication request from the Exchange Server, it presents a challenge originally created by the target server. Manipulating the Response: The client (Exchange Server) responds to this challenge, and the attacker can then take this response to continue NTLM negotiation with the target, such as a domain controller. Potential Access and Exploitation: Successfully executing this relay can allow the attacker to access resources or perform actions under the guise of the Exchange Server account. |
| 2406 | Suspected SMB packet manipulation (CVE-2020-0796 exploitation) | High | Vulnerability Announcement Date: The vulnerability was announced by Microsoft on March 12, 2020. Vulnerability Details: CVE-2020-0796 is a remote code execution vulnerability in the Microsoft Server Message Block 3.1.1 (SMBv3) protocol. SMB is a network file sharing protocol that allows applications on a computer to read and write to files and request services from server programs in a computer network. Nature of Vulnerability: The issue lies in the way SMBv3 handles certain types of requests. Exploitation: An attacker who successfully exploits this vulnerability can execute arbitrary code on the target server or client. This means that the attacker could potentially take control of the affected system. Affected Systems: Unpatched Windows servers that use SMBv3 are at risk. The vulnerability is particularly dangerous because it can be triggered remotely without requiring authentication or user interaction. Detection Mechanism: The specific detection you are referring to is triggered by Microsoft Defender for Identity. It identifies suspicious activities related to SMBv3 packets that may be attempting to exploit the CVE-2020-0796 vulnerability. Target of Attack: The attack targets a domain controller in the network. |
| 2416 | Suspicious network connection over Encrypting File System Remote Protocol | High or Medium | Exploiting the Encrypting File System Remote Protocol (EFSRPC): EFSRPC is designed to allow remote file operations, particularly related to the Encrypting File System (EFS) ④ in Windows, which provides file-level encryption. Adversaries target this protocol to perform unauthorized privileged file operations. Privilege Escalation in Active Directory Network: The core of the attack involves escalating privileges within an AD network. Active Directory is widely used for identity management and access control in Windows environments. Coercing Authentication from Machine Accounts: The attacker begins by coercing (manipulating) authentication requests from machine accounts. This can be done through various methods, like sending crafted network requests that force a machine to authenticate to an attacker-controlled system. Relaying to the Certificate Service: Once the attacker receives authentication requests, they relay these requests to the Active Directory Certificate Services. Taking Over the AD Domain: By chaining the exploitation of a flaw in the EFSRPC Protocol with a vulnerability in the AD Certificate Services, the attacker can potentially take over the AD domain. This means gaining control over domain accounts, policies, and access rights. Impact: The successful exploitation of this attack can lead to significant security breaches, including unauthorized access to sensitive data, compromise of administrative privileges, and potential lateral movement within the network. |
| 2414 | Exchange Server Remote Code Execution (CVE-2021-26855) | High | Vulnerability in Exchange Server: CVE-2021-26855 presents a significant security risk, as it allows unauthenticated remote code execution. This means that an attacker can remotely execute code on a device running Exchange Server without needing to authenticate. Attack Mechanism: This vulnerability is partially caused by the way the Exchange Server handles requests for static resources. Static resources are elements like scripts (.js) and images (.png) that are used to build and display web pages. In the context of an email server like Exchange, these resources need to be accessible even if a user hasn’t logged in or authenticated. This is common in web services to allow the basic functionality of web pages or to serve public content. However, this necessary feature can be exploited by attackers. Since these static resources are accessible without authentication, attackers can craft specific requests to these resources in a way that the server mistakenly treats them as legitimate or authenticated. Essentially, attackers exploit this behavior to bypass the normal authentication checks that would usually restrict access to sensitive operations or data. Impact: This vulnerability is a significant security risk because it allows attackers to execute code or access data on the server without needing proper credentials. |
| 2035 | Suspected WannaCry ransomware ⑤ attack | Medium | Non-Standard Protocol Implementation: The attack involves the use of tools that implement various protocols in ways that deviate from their standard, intended use. These protocols are typically part of network communications and file-sharing systems. Windows Acceptance of Traffic: This non-standard network traffic, although unusual, is often accepted by Windows systems without triggering any warnings. This means that the systems do not inherently recognize these activities as malicious. Indicative of Advanced Ransomware Techniques: The detected behavior is indicative of techniques used by advanced ransomware threats, like WannaCry. WannaCry is known for its ability to rapidly encrypt files on a victim’s computer and spread across networks, demanding ransom for the decryption key. |
| 2034 | Suspected use of Metasploit ⑥ hacking framework | Medium | Non-Standard Protocol Implementation: Same as 2035, 2033 Windows Acceptance of Traffic: Same as 2035, 2033 Indicative of Metasploit Use: The behavior detected is indicative of techniques associated with the Metasploit hacking framework. Metasploit is a popular tool among security professionals for penetration testing and vulnerability discovery but can also be used by attackers for malicious purposes. It is known for its ability to exploit vulnerabilities across various systems and protocols. |
① The Print Spooler service queues print jobs sent by users or applications. When a document is sent to print, it doesn’t go directly to the printer. Instead, it’s first processed and queued by the Print Spooler.
② MIC operates by generating a cryptographic hash over the sequence of messages exchanged during the authentication procedure, such as negotiation, challenge, and response. This hash is then verified by the receiving party to ensure that none of the messages have been altered or tampered with in transit. If the MIC check fails, it indicates a potential security breach, such as a man-in-the-middle attack, where an attacker intercepts and possibly modifies the messages.
③ NTLM v2 can mitigate relay attacks on authentication requests primarily due to its enhanced security features. Unlike NTLM v1, NTLM v2 incorporates both client and server nonces (random numbers) to create a unique session-specific challenge, making each authentication request distinct and tied to a particular session. Additionally, it includes specific target server information in the authentication process, effectively binding the authentication message to a specific server and session. This means that a response captured for one session cannot be easily reused or relayed in another session or to a different server. Furthermore, the inclusion of a timestamp in the NTLM v2 response helps to prevent replay attacks, ensuring that the authentication message is timely and valid only for a short period.
④ Encrypting File System is a feature in Windows operating systems that provides file-level encryption. It’s designed to protect sensitive data stored on a hard drive from unauthorized access. When viewing in Task Manager or other system monitoring tools, you will not see a process specifically named for the EFS service. Instead, the lsass.exe process is observed, which hosts EFS and other security-related functions.
⑤ WannaCry is a ransomware that caused a major global cyber attack in May 2017. WannaCry spread by exploiting the EternalBlue vulnerability in Windows SMB protocol. Unlike typical ransomware, WannaCry could autonomously propagate across networks. Victims were demanded to pay a ransom in Bitcoin.It affected hundreds of thousands of computers in over 150 countries.
⑥ Metasploit is a powerful and widely used framework for penetration testing and security vulnerability assessment.
T1550 Use Alternate Authentication Material
| External ID | Name | Sev. | Description |
| 2017 | Suspected identity theft (pass-the-hash ①) | High | Stealing NTLM Hashes: The attacker first acquires a user’s NTLM hash. This hash is essentially the encrypted form of the user’s password. Using the Stolen Hash: Instead of decrypting the hash to get the password, the attacker uses the hash itself to authenticate as the user on other computers within the network. |
| 2018 | Suspected identity theft (pass-the-ticket ②) | High | Stealing Kerberos Tickets: Attackers acquire a valid Kerberos ticket from a compromised system. Ticket Reuse: The stolen ticket is then reused to authenticate on other network computers as if the attacker were the legitimate ticket holder. Detection Indicator: A key sign of this attack is when the same Kerberos ticket is used on two or more different computers. |
| 2002 | Suspected overpass-the-hash ③ attack (Kerberos) | Medium | This alert is signaling a potential security incident related to the Kerberos authentication protocol. Specifically, it suggests that there might be an “overpass-the-hash” attack in progress or being attempted. |
① T1550.002 Pass the Hash is a cyber attack technique where adversaries use stolen password hashes to authenticate as a user within a network, bypassing the need for the user’s actual password. This method enables attackers to gain unauthorized access to both local and remote systems by directly using the captured hashes, circumventing normal authentication processes.
② T1550.003 Pass the Ticket is a cyber attack technique where adversaries use stolen Kerberos tickets for lateral movement within a network, effectively bypassing normal access controls. This method involves authenticating to systems using Kerberos tickets, obtained through methods like OS Credential Dumping, without the need for the account’s password. Attackers can use a user’s service tickets or a TGT to access resources or request additional service tickets for broader access. Advanced variations of this attack include the creation of ‘Silver Tickets’ for specific services and ‘Golden Tickets’ using the KRBTGT account NTLM hash for domain-wide access. Additionally, techniques like “overpassing the hash” involve using NTLM password hashes to create valid Kerberos tickets, combining Pass the Hash with Kerberos authentication to increase attack effectiveness.
③ Overpass-the-hash: This is a technique where attackers gain access to password hashes (encrypted passwords) and then use them to authenticate themselves, effectively bypassing the need to know the actual plaintext passwords.
Other Combined Tactics
| External ID | Name | Sev. | Description |
| 2047 | Suspected rogue Kerberos certificate usage | High | Persistence Technique: This attack is a method of maintaining unauthorized access within an organization’s network. Target of Compromise: The attack targets the Certificate Authority (CA) server within an organization. The CA is responsible for issuing and managing security certificates. Method of Attack: Once attackers gain control over the organization, they compromise the CA server. Generation of Rogue Certificates: After compromising the CA, attackers generate unauthorized certificates. Purpose of Rogue Certificates: These certificates serve as backdoor accounts, which can be exploited in future attacks. Impact: The use of rogue certificates allows attackers to masquerade as legitimate users or systems, bypassing security measures and gaining sustained access to the network. |
| 2033 | Suspected Brute Force attack (SMB) | Medium | Tools Implementing Protocols Non-Standardly: Attackers use tools (Hydra ①) that apply protocols like SMB, Kerberos, and NTLM in ways that deviate from their standard, intended use. These protocols are standard in Windows environments for tasks like network file sharing (SMB), authentication (Kerberos and NTLM), and more. Windows Acceptance of Traffic: This non-standard network traffic, although unusual, is often accepted by Windows systems without triggering any warnings. This means that the systems do not inherently recognize these activities as malicious. |
① Hydra, often referred to as “THC Hydra,” is a well-known tool in the field of network security. It’s primarily used for performing rapid dictionary attacks or brute-force attacks against various protocols and services.