Common AD FS Concepts Terminologies
The screenshots with watermark are sourced from the YouTube channel ‘Concepts Works‘, specifically featuring the Active Directory Federation Service – Office365 – YouTube video.
Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS)
Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS) is a service provided by Microsoft for enabling single sign-on (SSO) across different systems or applications. It allows users to access multiple systems using the same set of credentials, usually through a central identity provider.
Account Store/Attribute Store
Account Store or Attribute Store refers to directories or databases used by an organization to store user accounts and their associated attribute values. These stores typically hold information such as user credentials and additional user-related data.
Claims
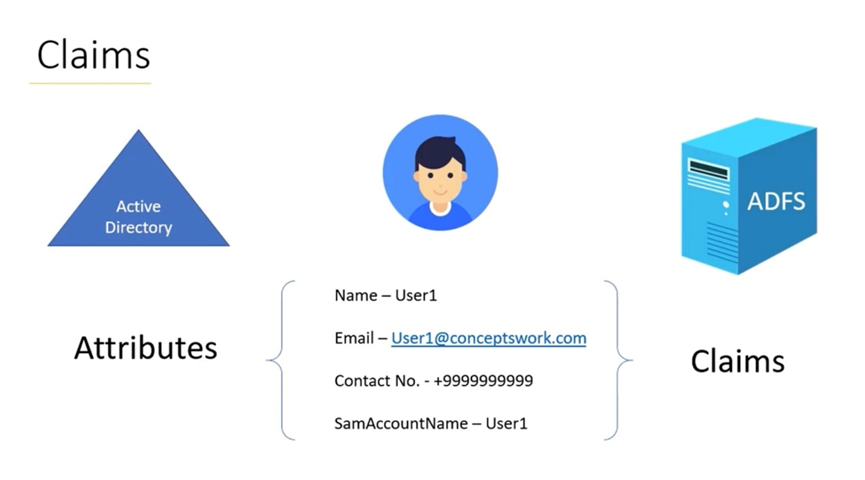
Claims can be considered as a set of Attributes, typically represent attributes or characteristics associated with a user, such as their name, email address, role, group membership, or any other relevant data.
Claims Provider
A Claims Provider, in the context of federated identity authentication services, is responsible for collecting and verifying user information, constructing claims, and packaging them into security tokens. ADFS itself can act as a typical Claims Provider.
The below screenshot shows that the claims provider is the Active Direcotry
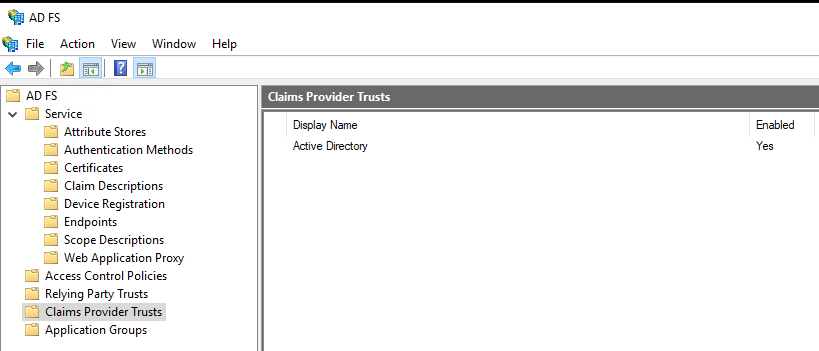
Claims Provider Trust
A Claims Provider Trust is another Claims Provider that ADFS trusts. It sends claims to ADFS based on Claims Rules and allows users from the trusted CP to access the relying party trusts configured in ADFS.
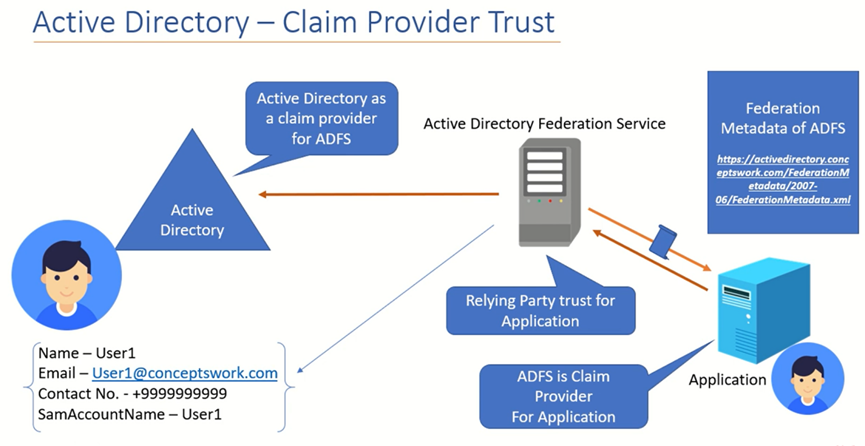
Relying Party (RP)
A Relying Party is the entity that consumes the claims, essentially the application or service that relies on ADFS for user authentication. The Relying Party requests and receives claims from the Claims Provider, and these claims may be transformed or mapped based on Claims Rules.
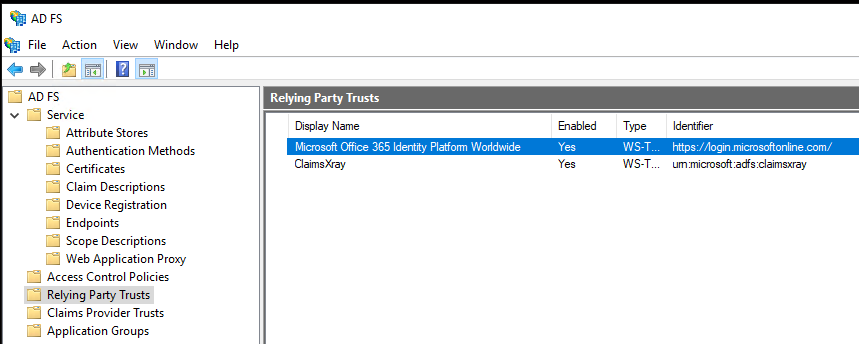
Relying Party Trust
Configured on the ADFS server is an application that will be contacting ADFS to handle authentication. ADFS validates the authentication requests received from applications with the help of relying party trusts. This validation is performed by verifying the Identifier value in the relying party trust, which should be the same as the one presented when the application sends the authentication request to your ADFS server.
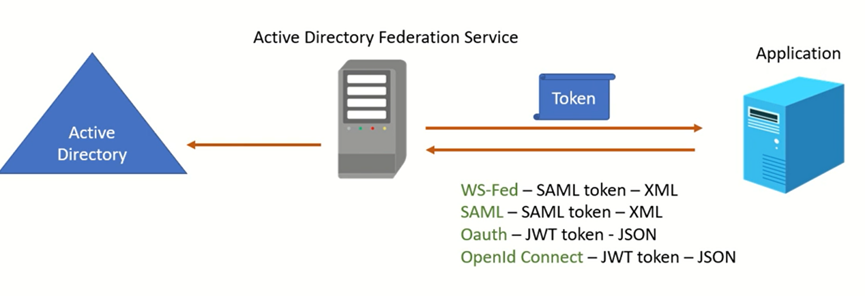
ADFS supports the following protocols: WsFed, SAML, OAuth, and OpenID Connect. These protocols enable seamless and secure authentication between the application and the ADFS server.
Claims Rule
A Claims Rule is a rule for transforming claims (executed by the Claim Engine). It determines that if the server receives claim A, it will issue claim B. The claims issued by ADFS to the relying party application are constrained by claim rules, which need to be pre-agreed upon and may involve transformation or mapping of claims.
Claim Issuance Policy
A crucial set of rules that determine the specific attributes or claims to be included in the authentication token. This policy precisely defines the claims that must be sent to the application during the authentication process.
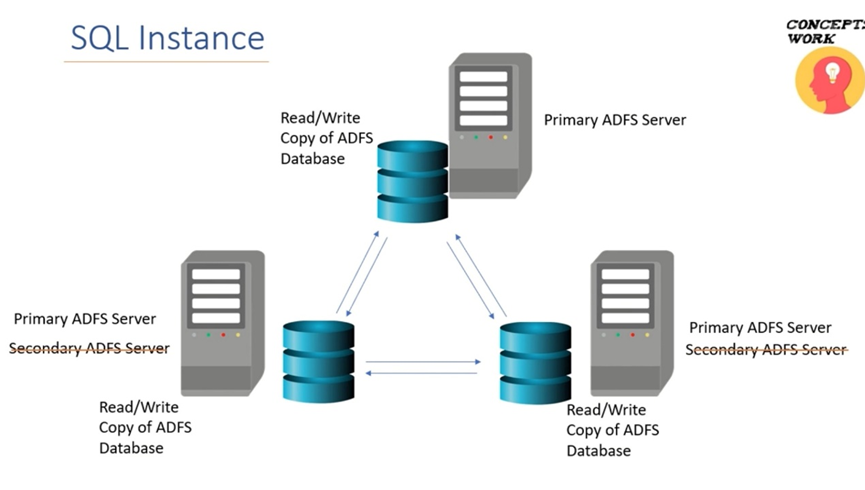
ADFS Database
A repository used by Active Directory Federation Services (ADFS) to store configuration settings, user information, trust relationships, and security-related data for federated identity authentication. It serves as a central storage for ADFS to manage and authenticate users across multiple applications and systems in a federated environment.
Windows Internal Database (WID)
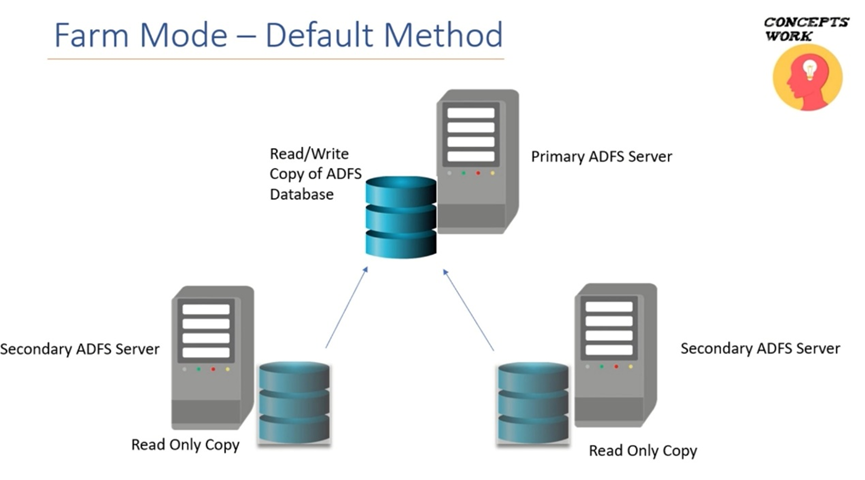
SQL Server